 The Eloquence Development Environment
The Eloquence Development Environment
Application Properties
The Application Properties dialog is used to configure the
global preferences of the IDE application. Some of the settings
can be overriden in a document specific
properties dialog.
The Application properties dialog can be accessed by selecting
the Application Propterties menu item from the View menu pane
or by pressing the associated accelerator keys ALT+0.
The Properties dialog provides several sections, which can
be accessed by selecting the corresponding tab at the top of the
dialog window.
Please note: All pathes are normalized automatically.
For example a backslash character, which is usually used in
Windows as a path separation character is converted to a slash.
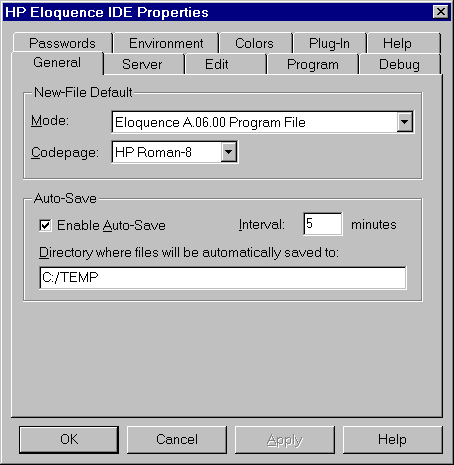
New-File Default
This setting is used to assign an initial file mode and code page
when opening a new editor window.
The following file modes are available:
- Eloquence Compatible Program File
This file mode is fully backward compatible, but the program file
size is limited to 64K. If the file size exceeds 64K, the A.05.01 file
mode is automatically applied.
- Eloquence A.05.01 Program File
With Eloquence A.05.01, this file mode has been added which
overcomes the 64K file size limit.
- Eloquence A.06.00 Program File
This is the new file format introduced with Eloquence A.06.00.
If the A.06.00 language extensions are used or the program file shall
be password-protected, this file mode is obligatory.
- Text File (CR-LF line separators)
- Text File (LF line separators)
- Text File (CR line separators)
The following code pages are available:
Please note, that the Eloquence editor only changes the character
set mapping (i.e. how a character is displayed), it does not change
the existing file contents. So it does not cause any problem to switch
the code page at any time. Any character entered is however mapped
according to the selected code page.
Auto-Save
The autosave feature is provided as a safety net to allow an emergency
recovery when "something" happens (according to Muphys law, there is
always a "something" that can go wrong). I would hate to loose my work
under any circumstances and we assume the same holds true for you too.
The autosave feature causes any modified content to be saved
to a temporary file after the configured interval exipres.
An autosave file is deleted automatically when the editor contents
is saved or discarded. The Autosave feature can be disabled individually
for each editor window (though the
Document Properties), as there are probably cases where you don't
want it for a particular document, for example when editing a huge file.
The path where autosave files are saved to is normally determined when
the Eloquence Development system starts. It defaults to the system
default location to hold temporary files (eg. C:\TEMP).
Autosave filenames consist of the following components:
- The original file name
- A unique idetifier, separated by a dot
- A trailing Autosave, seperated by a dot
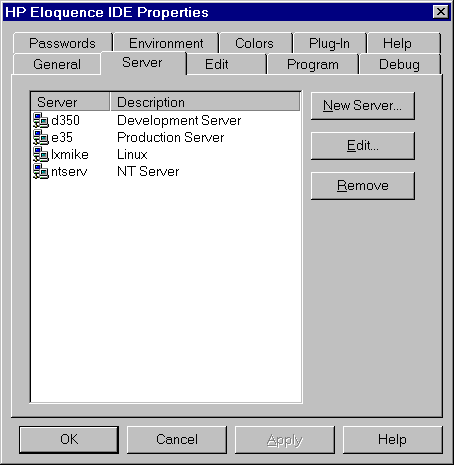
This dialog is used to configure the known Eloquence servers.
When configured, they will be displayed in the Explorer Window.
- To add a new server, select the NEW SERVER push button.
- To delete an existing server definition, select the server
name and select the REMOVE push button.
- To edit an existing server definition, either select the server
name and select the EDIT push button or double-click the server name.
The following dialog appears to define a server entry:
- Server Name
- The server hostname. You can also specify an IP address
(in the usual dot notation).
- Description
- An arbitrary server description
- Service
- The default service name is eloqsd. You can also specify a
port number.
- Login ID
- Enter your login id. THIS IS NOT YOUR HP-UX LOGIN ID.
The LoginID and password must have been configured in the eloqsd.user
file by the server administrator.
- Password
- Please enter the password for the given Login ID.
The password is mandantory and must be entered twice, both values
must match.
Please note:
Unless you use DNS, the server name must have been defined in your
hosts file.
The service name must have been defined in your services file.
The port number must be the same on the server and the
client system.
Please refer to the installation documentation for further reference.
This dialog pane can be used to configure the Editor defaults.
Specific settings can be configured for each editor window
in the Document Properties.
Category
All settings contained in this dialog pane are independently stored
for program- and text files, respectively. The category selector is
used to switch between the program and text file settings.
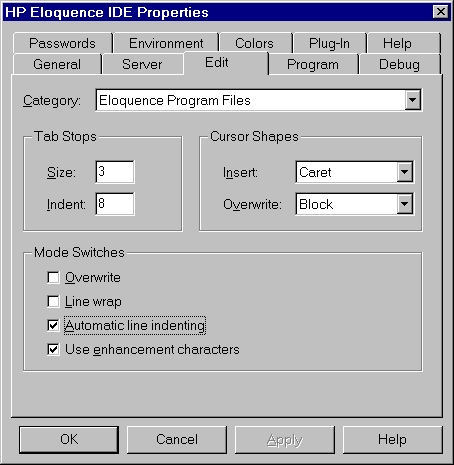
Tab Stops
The tab stop settings are used to define the tab positions.
Eloquence supports two different tab settings:
- The inital tab
- Any subsequent tab position
For Eloquence programs, these settings are used to define the
statement indent and structural indention.
Cursor Shapes
You can define the cursor shape the be used in the editor window
for insert and overwrite mode:
Mode Switches
This defines the default editor mode settings.
- In Overwrite mode, each character typed replaces an existing character
with the following exception:
- At the end of the line, new characters are added
- The RETURN key always inserts a line break
- The TAB key sets the cursor to the next tab position.
At the end of the line, spaces are added up to the next tab.
- The Backspace and DEL keys always remove a character.
- When enabling the Line Wrap mode, the editor window will wrap
a line at the current window border. An arrow is displayed at the right
margin. Some Eloquence program lines can get quite long and it can be
inconvenient to see only a subset of a line.
- When automatic line indenting is enabled and the RETURN key is hit,
the new line will start with the same indent as the previous line.
- With the "use enhancement characters" option enabled, all
enhancements such as character attributes and the line draw character
set are displayed and can be edited in the editor window.
This dialog pane can be used to configure the defaults for
program files.
Specific settings can be configured for each editor window
in the Document Properties.
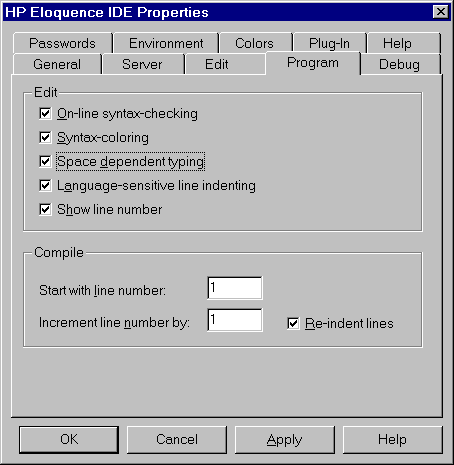
Edit
The edit settings are used to define the behavior of the editor
when working with program files:
- On-line syntax-checking
When enabled, each time the cursor leaves a modified program line,
the syntax is checked.
If a syntax error is detected, the error description is shown in
the status bar and the program line is highlighted in the
configured error color.
- Syntax-coloring
When enabled, colors are used to enhance the program source code.
Please Note: On-line syntax-checking must be enabled in order
to use syntax-coloring.
- Space dependent typing
When enabled, the on-line syntax-checking will work in space dependent
mode. In this mode, separating spaces are significant while upper- or
lowercase is not.
Please Note: On-line syntax-checking must be enabled in order
to use space dependent typing.
- Language-sensitive line indenting
When enabled and the RETURN key is hit, the new line is indented according
to the meaning of statement contained in the previous line (e.g. the line
after a SUB statement is automatically indented).
Please Note: On-line syntax-checking must be enabled in order
to use language-sensitive line indenting.
- Show line number
This activates an indicator in the status bar where the current line
number is diplayed. The indicator can also be used to navigate to a
specific program line.
Compile
The compile settings define how the compiler acts on program files:
- Start with line number
- Increment line number by
When a program is compiled, all lines are renumbered. These settings
define how this takes place.
- Re-indent lines
When enabled, all lines are automatically re-indented on compilation.
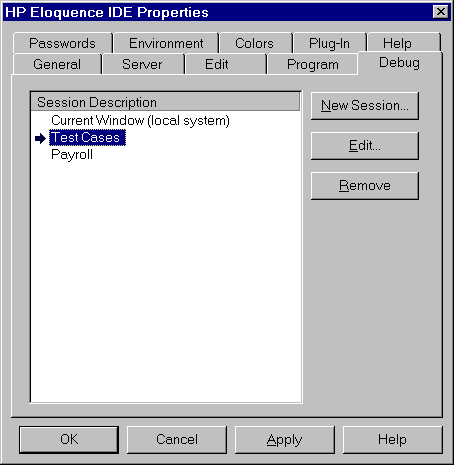
- The current debug configuration is marked by an arrow.
- To add a new debug configuration, select the NEW SESSION push button.
- To delete an existing debug definition, select the session description
and select the REMOVE push button.
- To edit an existing debug definition, either select the session
description and select the EDIT push button or double-click the session
description.
The following dialog is used to define a debug configuration:
- Server
- The server where the debug process should be executed on.
The entry "Local System" indicates a local debug session.
- Command
- The commandline passed to the debug process.
Commandline arguments are separated by spaces.
Arguments containing spaces can be enclosed in double quotes.
- Execute current window
- When enabled, the file name of the topmost editor window
is appended to the commandline. This enables a single debug
session configuration to be applied to different programs.
Please note: When using this setting, the Server must be
switched to "Local System" and the Command must not refer to any
program file.
Please note: This setting requires the topmost window
to be an editor window containing a program file.
- Environment
- Environment variables passed to the debug process.
Environment variable assignments must have the form of
VAR=value and are separated by spaces.
Values containing spaces can be enclosed in double quotes.
- Start Directory
- The Start Directory can be used to define an initial
current directory, when the eloqcore process is started.
By default, eloqcore will inherit the current directory from
eloqsd.
- TTY Device
- This is an experimental entry which can be used to provide debug
support for character oriented Eloquence programs (when executed
on a UNIX server). When set, this entry is used to assign stdin,
stdout and stderr of the debug process. It must be an absolute path
to an existing file and probably makes only sense if this is
a tty device file.
This setting has no effect when a debug session is run on
the Windows platform.
To obtain the tty devicefile name to debug a character oriented
Eloquence program, you could use one of the following:
- Use a terminal device connected to a serial device. You should not
run a getty on this port and you must configure it properly before
using it. In this case, simply enter the tty device file (for example
/dev/tty0p1).
- - or -
- Login to your server system
- Obtain the tty device using the tty command.
The device file is typically similar to /dev/ttyp4.
- Disable the shell input (for example by executing a sleep 10000)
- Enter the device file in the configuration.
When starting the debug process, it should be connected to
the specified device.
(Yes, I know - this is complicated. We are looking for a way to make
this easier and even automatic.)
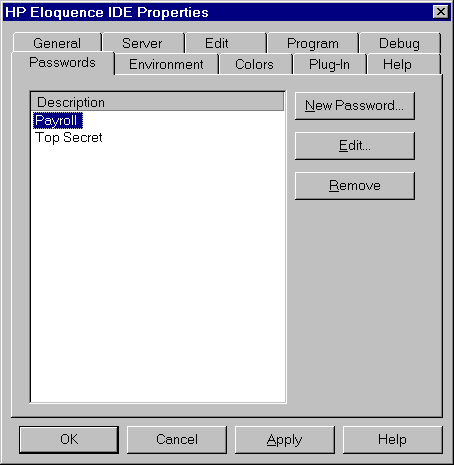
With Eloquence A.06.00, program files can be password-protected.
The password configuration enables you to configure a list of frequently
used passwords. When a password-protected program is loaded, all the
passwords configured here are automatically checked. This way, working
with password-protected programs becomes as convenient as possible.
For further reference, please refer to the section
Working with password-protected files.
- To add a new password, select the NEW PASSWORD push button.
- To delete an existing password, select the password description
and select the REMOVE push button.
- To edit an existing password, either select the password
description and select the EDIT push button or double-click on the
password description.
The following dialog is used to define a password configuration:
- Description
- This description should point out what purpose this password
shall serve.
- Password
- The password is mandantory and must be entered twice, both values
must match.
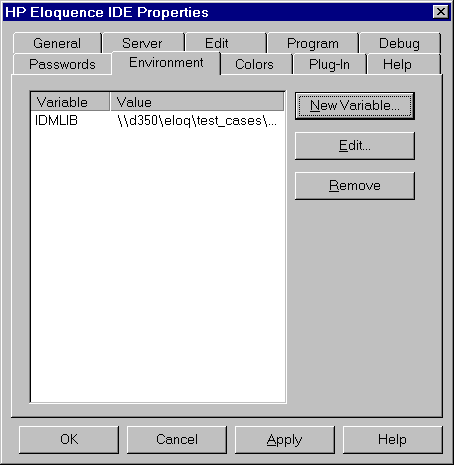
Environment variables can be used during runtime to locate dialog
files. To enable the integrated dialog editor to locate dialog
files in a similar manner, variables can be defined which resemble
the runtime environment.
- To add a new variable, select the NEW VARIABLE push button.
- To delete an existing variable, select the variable name from
the list and select the REMOVE push button.
- To edit an existing variable, either select the variable
name and select the EDIT push button or double-click on the
variable name.
The following dialog is used to define a variable:
- Variable
- The variable name
- Value
- The associated value
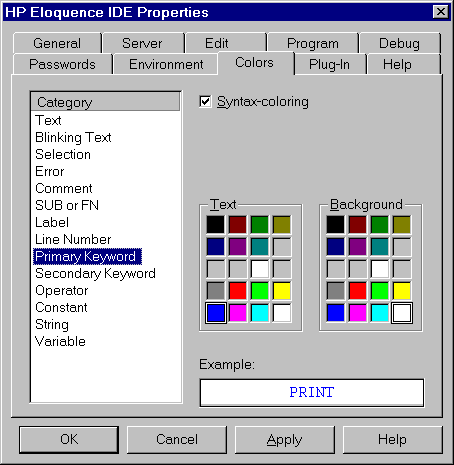
The Eloquence editor uses colors to enhance the display
of various elements. This dialog can be used to configure the
used colors.
The box on the left side provides all categories, for which colors
usage can be configured.
The Example field visualizes a sample content in the selected colors.
You can configure the foreground and background colors individually
from the System palette.
When "Syntax-coloring" is checked, colors are used to enhance the
program source code in the editor. This is also reflected in the
Program settings.
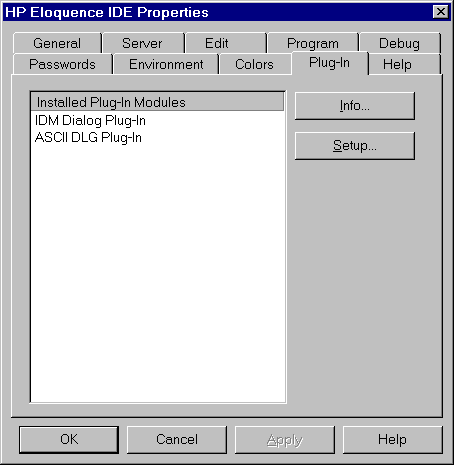
The integrated dialog editor uses plugin modules to handle various
dialog formats. A plugin is responsible for loading and storing
the resource file and translate it into or from the internal editor
format. When the IDE is started, it locates the available plugins.
This dialog provides access to plugin version information and
plugin specific configuration settings.
- To get version information on a plugin, please select the
plugin from the list and select the Info pushbutton.
- To open the configuration dialog for a plugin, please select the
plugin from the list and select the Setup pushbutton.
When information on a plugin is requested, a dialog like below will
appear:
The following dialog plugins are available:
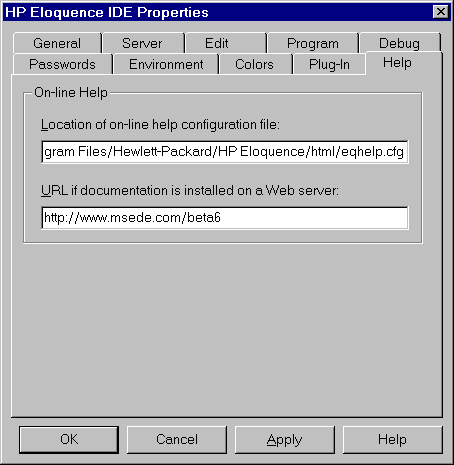
The Eloquence needs a help configuration file (eqhelp.cfg) to
locate the online help. The path to the eqhelp.cfg file is normally
determined automatically when the Development Environment is started
and defaults to the html subdirectory of the installation directory.
In order to use a different directory, you can provide the absolute
path to the configuration file.
All help files are accessed relative to the configuration file.
In a future release, you will be able to integrate your own
online documentation with the Eloquence and handle it in a
consistent manner.
© Copyright 1997 Hewlett-Packard GmbH. All rights reserved.
Revision: 98/02/18
 The Eloquence Development Environment
The Eloquence Development Environment