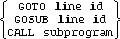





6 Branching and Subroutines
NOTE: Softkeys can't be used together with the graphical user interface and so it is not supported on Windows platforms.
ON KEY# key number, [#key number 2 , ... , # key number n] [:"label"]
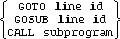
NOTE: Although a subprogram may be CALLed using the ON KEY # statement, no parameters may be passed.
The key number is an integer expression from 1 through 24. Multiple keys can be defined within the same ON KEY # statement.
When a key is pressed and an ON KEY # has been declared for it, the specified branch is made after the current line has been executed. The optional label is a string expression; the first 18 characters of it appear above the defined softkeys (keys 1 through 8), so labelling the softkeys on the screen.
ON KEY # statements which specify GOTO or GOSUB are active only in the program segment in which they were declared.
NOTE: The eighteenth character of the last function key in each of the three sets (8, 16, and 24) cannot be displayed on some terminal types (for example, the HP 700/92). Therefore, avoid assigning an eighteen character long label to softkeys 8, 16, and 24.
As an example, here is a program sequence which defines some of the softkeys, allowing the operator to select the desired routine:
10 OFF KEY #3,4,5,6,7
20 ON KEY #1,#9,#17:"START APPLICATION" GOTO Init
30 ON KEY #2:"ENTER CONFIG" GOTO Config_applic
40 ON KEY #8:"EXIT" GOTO Halt1
50 PRINT PAGE,LIN(10),SPA(20),"APPLICATION STARTUP"
60 PRINT SPA(20), "SELECT OPERATION BELOW"
70 WAIT ! Wait for softkey.
80 Init: ! Start application.
90 ON KEY #1,#9,#17:"ACCOUNTING" GOTO Key1
100 ON KEY #2:"ORDERING" GOTO Key2
110 ON KEY #7:"RESTART" GOTO 10
120 PRINT PAGE,LIN(10),SPA(20),"SELECT MODULE TO BE
STARTED BELOW"
130 WAIT ! Wait for softkey.
140 Config_applic: ! Enter application parameter.
.
.
.
Line 10 cancels any previous ON KEY # definitions for keys 3 through 7. Lines 20 through 40 define the keys for initial selection. The program then displays instructions and waits at line 70 until a defined softkey is pressed. The Init routine, lines 80 through 130, show how softkey 1 and softkey 2 are redefined and how softkey 7 is defined to restart the program. The previous definition for softkey 8 remains in effect here. Another WAIT statement holds program execution until a defined softkey is pressed.
OFF KEY # [key number list]
Omitting key numbers causes all ON KEY # definitions to be cancelled. See line 20 in the preceding example program.
DISABLE
The ON KEY # declaratives are still active; pressing each softkey causes the interrupt to be logged for execution when the declaratives are re-enabled.
ENABLE
The possible values returned by CURKEY, and their meaning, are given here:
The CURKEY value is cleared by any SCRATCH operation and by pre-run initialization (RUN, GET, etc.).
Here is a simple program which defines the softkeys 1 through 8 and then displays each softkey number pressed.
10 FOR Key=1 TO 8 11 A$=VAL$(Key) 20 ON KEY #Key:A$ GOSUB 50 30 NEXT Key 40 WAIT 50 DISP "KEY";CURKEY;"PRESSED" 60 RETURN
SOFTKEYSET ON
SOFTKEY SET OFF
U1 - U3 user keys (ON KEY #) S1 - S2 system
The SOFTKEYSET statement will switch softkeys to the level given by the SOFTKEYSET expression: