




14 Integrating C Functions (DLL)
First write the C functions you want to call from your Eloquence application.
Then start the program /usr/eloquence/dllcc. This program analyzes the C functions and determines the function names and arguments which have to be used in the CALL DLL statement. This information is stored in a second C source file.
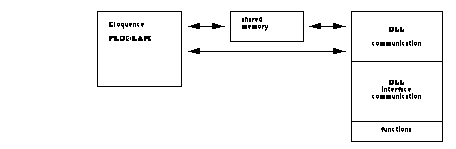
Now compile all C source files using the ANSI-C option and link them with the library libeloq.a. LOAD DLL starts the DLL process and initializes the shared memory.
The DLL program is started as a separate process from within Eloquence to prevent mutual interference.
The DLL process now waits for a signal from Eloquence. CALL DLL copies the arguments into shared memory and signals the DLL process that the arguments have been passed. Now control is passed to your C function. The DLL process converts the passed arguments into the format specified in the C functions. If the return value of the C function is non-zero, this value is used to force an Eloquence error. If no error has occured the DLL function transfers the arguments passed as "passed by reference" back to the shared memory segment and signals the Eloquence process that the DLL function has finished.

NOTE: ANSI-C functionality is not supported by the C-compiler provided as part of the standard HP-UX operating sytem. It is supported by the C-compiler sold as an optional, separate product. See the example in the directory /usr/eloquence/example of how to compile a DLL without the optional ANSI-C compiler. The example DLL described in this manual is generated using the ANSI-C compiler.
Options:
Examples:
dllcc -o sampleif.c sample1.c sample2.c cat test.c | dllcc - >testif.cEach source file containing functions to interface with Eloquence must include the file dllif.h.
Each user function you want to call from Eloquence must be of type EqDLL.
The function arguments must be of the following type:
C comments (/*...*/) are recognized and ignored.
The C preprocessor statements
#if 0 ... #endifcan be used to deactivate whole segments, but they must not be nested.
The function syntax must follow the ANSI-C convention:
EqDLL functionname ( EqVoid )
EqDLL functionname ( Argument [, Argument] )
EqDLL functionname ( Argument [, Argument [,...]] , ...)
Argument types:
EqInt ArgumentName
This is an Integer argument which cannot be modified ("pass by value"). Valid argument types are INTEGER, DINTEGER, SHORT, REAL
EqInt *ArgumentName
This is an Integer argument which can be modified or an Integer array ("pass by reference"). Valid argument types are INTEGER, DINTEGER
EqInt ArgumentName size
This is an Integer array ("pass by reference"). If size is specified, this array must at least have size elements. Valid argument types are INTEGER, DINTEGER.
EqReal ArgumentName
This is a Real argument which cannot be modified ("pass by value"). Valid argument types are INTEGER, DINTEGER, SHORT, REAL.
EqReal *ArgumentName
This is a Real argument which can be modified, or a Real array ("pass by reference"). Valid argument types are SHORT, REAL.
EqReal ArgumentName size
This is a Real array ("pass by reference"). If size is specified, this array must at least have size elements. Valid argument types are SHORT, REAL
EqChar *ArgumentName
This is a pointer to a zero-terminated character array ("pass by value"). Valid argument type is STRING.
EqString *ArgumentName
This is a String argument which can be modified or a String array ("pass by reference"). Valid argument type is STRING.
EqString ArgumentName size
This is a String array ("pass by reference"). If size is specified, this array must have at least size elements. Valid argument type is STRING
...
This is a variable argument ("pass by reference"). Type depends on the Eloquence data type passed. A maximum of 20 arguments can be passed. Example:
/* num.c */
#include "dllif.h"
EqDLL int_add( EqInt int1, EqInt int2, EqInt *result )
{
*result = int1 + int2;
return(0);
}
EqDLL int_div( EqInt int1, EqInt int2, EqInt *result )
{
if(int2 == 0)
return(31); /* division by zero */
*result = int1 / int2;
return(0);
}
The call
dllcc -o num.if.c num.ccauses dllcc to generate the file num.if.c with the following content:
Example:
/*
num.if.c
THIS FILE IS GENERATED AUTOMATICALLY BY DLLCC
DON'T CHANGE MANUALLY
*/
#include <dllif.h>
/*
int_add( long int1, long int2, long *result )
int_div( long int1, long int2, long *result )
*/
struct EqFuncList EqFuncList[] = {
{ "int_add", 0, 3 },
{ "int_div", 3, 3 },
{ 0L }
};
struct EqArgList EqArgList[] = {
{ "int1", EqArg_IntByValue , 0 },
{ "int2", EqArg_IntByValue , 0 },
{ "result", EqArg_IntByReference , 0 },
{ "int1", EqArg_IntByValue , 0 },
{ "int2", EqArg_IntByValue , 0 },
{ "result", EqArg_IntByReference , 0 },
};
int EqCall(fn, av)
int fn; void *av[];
{
switch(fn) {
case 0:
return int_add(*(EqInt *)(av[0]), *(EqInt *)(av[1]), (EqInt *)(av[2]));
case 1:
return int_div(*(EqInt *)(av[0]), *(EqInt *)(av[1]), (EqInt *)(av[2]));
default:
return -1;
}
}
This is the sample 'makefile' to build the above example.
Example:
# compiler flags
CFLAGS = -Aa +OV
Num: num.o num.if.o
$(CC) -o $@ $(CFLAGS) num.if.o num.o -leloq -lmalloc
num.if.o: num.c
/usr/eloquence/dllcc -o num.if.c num.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c -o $@ num.if.c
rm -f num.if.c
The corresponding Eloquence application is NUM.PROG.
Example:
1000 ! RE-STORE "NUM,EXAMPLE"
1010 !
1020 INTEGER Res
1030 !
1040 ON ERROR GOSUB Error
1050 !
1060 LOAD DLL Num,"Num,EXAMPLE",1024
1070 !
1080 CALL DLL Num("int_add",1,1,Res)
1090 PRINT Res
1100 CALL DLL Num("int_div",5,2,Res)
1110 PRINT Res
1120 CALL DLL Num("int_div",1,0,Res)
1130 PRINT Res ! Value unchanged due to error
1140 !
1150 DEL DLL Num
1160 END
1170 !
1180 Error:!
1190 PRINT ERRM$
1200 PRINT ERRMSG$(ERRN)
1210 RETURN
#include dllif.h
struct EqFuncInfo *EqFuncInfo( void )This function returns information about the current function.
Type EqFuncInfo is defined in dllif.h.
struct EqFuncInfo {
char *name;
int arg_cnt;
};
name contains a pointer to the function name. arg_cnt contains the number of arguments.
This data must not be modified.
struct EqArgInfo *EqArgInfo( void *arg )This function returns information about a function argument. If the argument is a pointer, it can be used to find out further information on this argument. Alternatively, the order (beginning at 0) can be passed.
If the argument is invalid, NULL is returned.
Type EqArgInfo is defined in dllif.h.
struct EqArgInfo {
enum EqArgType type;
char *name;
int elcnt;
};
type specifies the argument type. name contains a pointer to the name of the argument. For a variable argument this is "...".
elcnt contains the number of elements. Unless the argument is an array, this is 1.
This data must not be modified.
int EqStrlen ( EqString *s);
Returns current string length of Eloquence string
int EqMaxStrlen( EqString *s);
Returns maximum string length of Eloquence string
int EqStrcat( EqString *s1, EqString *s2);
Appends a copy of string s2 to the end of string s1. Returns zero on success or 18 on string overflow.
int EqStrcpy( EqString *s1, EqString *s2);
Copies string s2 to string s1. Returns zero on success or 18 on string overflow.
int EqStrcmp( EqString *s1, EqString *s2);
Compares its arguments and returns an integer less than, equal to, or greater than zero, depending on whether string s1 is lexicographically less than, equal to, or greater than string s2.
EqString *EqSubstr( EqString *s, int start, int len);
Extracts substring of Eloquence string.
start is the position of the first character starting at 1
len is the number of characters to be extracted.
Returns new Eloquence string descriptor, or NULL pointer if arguments are invalid.
NOTE: The return value points to a static area which will be overwritten on next call. The string value is not moved; the descriptor will point into original string.
int EqStr2str( EqString *eq, void *s);
Converts Eloquence string into zero terminated string. Returns string length without trailing zero.
NOTE: Target string must provide enough space to hold string value and terminating \0 character.
int str2EqStr( void *s, EqString *eq);
Converts zero terminated string into Eloquence string. Returns zero on success, or 18 on string overflow.
Allocate new string using malloc(). Returns NULL on memory allocation failure.
NOTE: The return value points to a static area and will be overwritten on next call.
void dll_setup( void ) void dll_cleanup( void )The DLL process can be terminated in dll_setup() or dll_cleanup() using exit().
To terminate the process while inside a function called by Eloquence, the process should send itself a SIGTERM signal (e.g. raise(SIGTERM); ). This is necessary to clean up properly.
Stderr is linked to the terminal but not integrated into the Eloquence screen buffer.
If you reroute stderr when starting Eloquence, for example for the purpose of external tracing, all output onto stderr will also be rerouted into this file.
DLL debug levels
0 = no debugging
1 = function call and return value
2 = function call, argument values, return value
3 = internal
Make sure that the file .xdbrc is present in your HOME directory, and that it contains the following:
z 17 rsAll modules of the DLL process must be compiled and linked using the debug option (-g).
You will need 2 terminals or 2 windows. No further user can have loaded the DLL.
Now start the Eloquence program on terminal 1. After the LOAD DLL statement has been executed, you can look up the process number of the DLL process using the 'ps' command.
Now start xdb on terminal 2 using the following options:
xdb -P {DLL process number} {DLL filename}
Insert a breakpoint in the routine(s) you want to test and continue the DLL process with xdb 'c' command. Now continue the Eloquence program execution on the first terminal. After the CALL DLL statement you are in debug mode.
3 functions are available:
int dll_main( void )dll_main() is called in a CALL DLL. The return code is interpreted as an Eloquence runtime error number.
void dll_init( void ) void dll_exit( void )These functions are called when the DLL process is started or terminated.
int u_get_argc( void )Returns the number of Eloquence arguments.
t_DLL_arg u_get_arg(int idx)Returns the description of an Eloquence argument.
u_unref_arg(int idx)Flags an argument passed as "pass by reference" as not modified (for TRACE).
Example:
/*
This is a sample DLL communication level routine
It will force eloquence runtime error with the error
number given as argument.
*/
#include <dll.h>
int dll_main( void )
{
int argc;
t_DLL_arg arg;
/* get argument count */
argc = u_get_argc();
if(argc != 1)
return(9);
/* check for integer argument */
arg = u_get_arg(0);
if(arg.type != DLL_INTEGER)
return(8);
if(arg.elcnt != 1)
return(8);
/* return error number */
return(*(int *)arg.ptr);
}