




3 Eloquence Graphical User Interface
DLG SET ".driver","motif"This will redirect output to your display as defined in the DISPLAY environment variable. If the DISPLAY environment variable is not set or if you want to output to a different display you can specify the display address in the driver command using the -display argument.
The driver provides a method to lookup additional arguments in a user-defined section of your eloq.ini file. Using this method, you can maintain system-specific driver arguments at a centralized location (eloq.ini), so you can execute your Eloquence program in different environments without code changes.
Example:
[myoptions] Arguments = -display client:0This enables an additional Dialog Manager argument which specifies a different output display client:0 where motif.drv will send its output to. In order to activate this item, the name of your user-defined section must be specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement, e.g.:
DLG SET ".driver","motif myoptions"NOTE: For details about configuration items and user-defined sections please refer to chapter Configuring Eloquence, section Customize the ELOQ.INI File on the HP-UX System.
Driver arguments can also immediately be specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement. This is useful for arguments which are closely related to motif.drv and not system-specific, e.g.:
DLG SET ".driver","motif myoptions -IDMfont 0 -IDMcolor 0"These two Dialog Manager arguments set the font and color resources to variant 0, this is normally appropriate for motif.drv.
NOTE: If driver arguments are immediately specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement, an user-defined section must be specified, too. However, if you specify a section name not present in the eloq.ini file, the user-defined section will be ignored.
NOTE: For a list of valid command line arguments, please refer to the ISA Dialog Manager documentation.
NOTE: The alpha.drv is different from Eloquence DLG since alpha.drv uses the Dialog Manager runtime functionality while DLG is a built-in Eloquence component.
Normally, text terminals are directly attached to the system running Eloquence, so DLG performs better compared to alpha.drv due to the alpha.drv client-server protocol overhead. For this reason, it is recommended to use Eloquence DLG for text terminals unless you need native Dialog Manager functionality.
DLG SET ".driver","alpha"This will redirect output to your display as defined in the DISPLAY environment variable. If the DISPLAY environment variable is not set or if you want to output to a different display you can specify the display address in the driver command using the -display argument.
The driver provides a method to lookup additional arguments in an user-defined section of your eloq.ini file. Using this method, you can maintain system-specific driver arguments at a centralized location (eloq.ini), so you can execute your Eloquence program in different environments without code changes.
Example:
[myoptions] Arguments = -display /dev/tty0p6This enables an additional Dialog Manager argument which specifies a different output display /dev/tty0p6 where alpha.drv will send its output to. In order to activate this item, the name of your user-defined section must be specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement, e.g.:
DLG SET ".driver","alpha myoptions"NOTE: For details about configuration items and user-defined sections please refer to chapter Configuring Eloquence, section Customize the ELOQ.INI File on the HP-UX System.
Driver arguments can also immediately be specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement. This is useful for arguments which are closely related to alpha.drv and not system-specific, e.g.:
DLG SET ".driver","alpha myoptions -IDMfont 2 -IDMcolor 2"These two Dialog Manager arguments set the font and color resources to variant 2, this is normally appropriate for alpha.drv.
NOTE: If driver arguments are immediately specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement, an user-defined section must be specified, too. However, if you specify a section name not present in the eloq.ini file, the user-defined section will be ignored.
NOTE: For a list of valid command line arguments, please refer to the ISA Dialog Manager documentation.
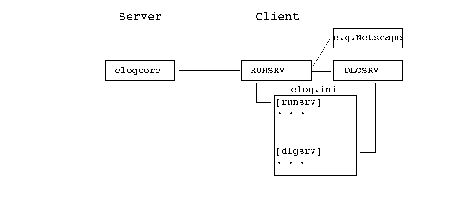
DLG SET ".driver","@client"where client is the name of the system running Microsoft Windows where the user interface (dialog server) should run.
NOTE: Client must be defined in your /etc/hosts file. You may also use the IP address instead of the host name.
When starting the network driver, you can pass additional arguments to the Dialog Manager runtime system. The driver provides a method to lookup additional arguments in an user-defined section of your eloq.ini file. Using this method, you can maintain system-specific driver arguments at a centralized location (eloq.ini), so you can execute your Eloquence program in different environments without code changes.
Example:
[debug] Arguments = -IDMtracefile C:\TMP\IDMTRACE.TXTThis enables an additional Dialog Manager argument which creates a trace file for debugging purposes. In order to activate this item, the name of your user-defined section must be specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement, e.g.:
DLG SET ".driver","@client debug"NOTE: For details about configuration items and user-defined sections please refer to chapter Configuring Eloquence, section Customize the ELOQ.INI File on the PC Platform.
Driver arguments can also immediately be specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement. This is useful for arguments which are closely related to the network driver and not system-specific, e.g.:
DLG SET ".driver","@client myoptions -IDMfont 1 -IDMcolor 1"These two Dialog Manager arguments set the font and color resources to variant 1, this is normally appropriate for the Microsoft Windows network driver.
NOTE: If driver arguments are immediately specified in the DLG SET ".driver" statement, an user-defined section must be specified, too. However, if you specify a section name not present in the eloq.ini file, the user-defined section will be ignored.
NOTE: For a list of valid command line arguments, please refer to the ISA Dialog Manager documentation.
This is the recommended method to start-up the network driver.
If you choose this method to start-up the network driver, DLGSRV expects a command line argument of -connect servername:portnumber which enables DLGSRV to connect to the server system (running Eloquence).
Using this nonstandard method to start-up the network driver is not recommended.
NOTE: Additional information is provided in section The DLGSRV Utility later in this chapter.
Starting the RUNSRV Utility
If you start RUNSRV.EXE on the remote PC, it will minimize itself waiting for a request.
If you restore the RUNSRV window, a log of the recent operations performed by RUNSRV is displayed. If RUNSRV is unable to handle a request, a message box pops up.
NOTE: RUNSRV uses the WINSOCK.DLL on the PC to interface the network software.
Common Problems
Network software not loaded
You either did not load the required network software or your network software is not compatible.
Service runsrv (tcp) not found in your SERVICES file
You did not install the runsrv service name in your SERVICES file.
Address already in use
The port number you used by RUNSRV is already in use. This may happen if the port number is not unique or if you try to run RUNSRV a second time.
WinExec failed (nn): Error Message
RUNSRV was unable to perform the requested operation. Error number and message reflect a problem detected by Microsoft Windows.
The Remote PC ELOQ.INI File
RUNSRV uses the configuration information of the [runsrv] section in the eloq.ini file on the PC. This file is located in your WINDOWS directory.
NOTE: Please refer to chapter Configuring Eloquence, section Customize the ELOQ.INI File on the PC Platform, Section [runsrv] for details.
NOTE: Please refer to the chapters Installing Eloquence and Configuring Eloquence for details about installation and PC platform prerequisites. (see chapter , Configuration of the GUI Server,)
Starting the DLGSRV Utility
Normally, DLGSRV is started automatically by the RUNSRV utility, which will provide the appropriate command line arguments. This is done when a DLG SET ".driver","@client" statement is issued. RUNSRV then uses the configuration item DlgSrvX or DlgSrv of the [runsrv] section in the eloq.ini file on the PC to compose the appropriate command line to start DLGSRV.
NOTE: Please refer to chapter Configuring Eloquence, section Customize the ELOQ.INI File on the PC Platform, Section [runsrv] for details about DlgSrvX and DlgSrv. Additional information is provided in How to Run Multiple DLGSRV Simultaneously later in the current section.
NOTE: DLGSRV uses the WINSOCK.DLL on the PC to interface the network software.
However, if the nonstandard method of manually starting DLGSRV is used, DLGSRV expects a command line argument of -connect servername:portnumber which enables DLGSRV to connect to the server system (running Eloquence):
DLGSRV.EXE -connect servername:portnumber [arguments]
When DLGSRV starts up, it will minimize itself. If you restore the DLGSRV window, a message box pops up, which allows you to terminate the DLGSRV program. This may also be achieved by selecting Close from the system menu.
NOTE: You should not terminate DLGSRV this way since this may lead to loss of data and abnormal termination of the server program. DLGSRV will be terminated automatically by Eloquence when processing has finished.
However, to recover from program failure or communication breakdown this method of manually terminating DLGSRV provides a very useful "emergency exit".
The Remote PC ELOQ.INI File
DLGSRV uses the configuration information of the [dlgsrv] section in the eloq.ini file on the PC. This file is located in your WINDOWS directory.
NOTE: Please refer to chapter Configuring Eloquence, section Customize the ELOQ.INI File on the PC Platform, Section [dlgsrv] for details.
How to Run Multiple DLGSRV Simultaneously
It is not possible to have more than one running instance of the Eloquence network dialog server for Microsoft Windows (DLGSRV). This is a limitation of Microsoft Windows which is not capable to deal with multiple instances of 16bit applications which have multiple writable data segments. In the past, any try to execute a second dialog server resulted in a WinExec error 16.
In order to overcome this limitation (which would prevent you from starting more than one graphical application simultaneously) a workaround has been implemented in Eloquence.
Microsoft Windows recognizes an application by its module identifier. A module identifier is simply a string at a known location in the executable file holding the internal application name. On application start-up, the Windows kernel checks if an application with this module identifier is already running. This has runtime benefits since the code segments of multiple instances are shared in memory.
The workaround to overcome this limitation is implemented by two means:
replace it with:
DlgSrvX = C:\ELOQ\DLGSRV%s.EXE -connect %s -IDMfont 1 -IDMcolor 1
NDlgSrv = 4
NOTE: The DlgSrv configuration item serves for backward compatibility and may not be supported in future releases anymore. DlgSrvX is much more flexible and should be used instead.
NOTE: Please refer to chapter Configuring Eloquence, section Customize the ELOQ.INI File on the PC Platform, Section [runsrv] for details about DlgSrvX and NDlgSrv.
The 32bit version supports the same functions as the 16bit version, so read the section above for further details. The differences are explained below.
NOTE: The RUNSRV32 utility will become obsolete in future releases. Its
functionality will be integrated into the eloqd server process.
The DLGSRV32 and RUNSRV32 programs get the configuration from the eloqcl.ini configuration file, which is located in the 'etc' directory of the Eloquence installation directory.
The DLGCLONE utility is obsolete since DLGSRV32 can be natively used in multiple instances.