 The Eloquence Development Environment
The Eloquence Development Environment
The Application Window
This document explains the basic components of the Eloquence
Development environment. Most things should be familiar to you,
if you have worked with Windows programs before.
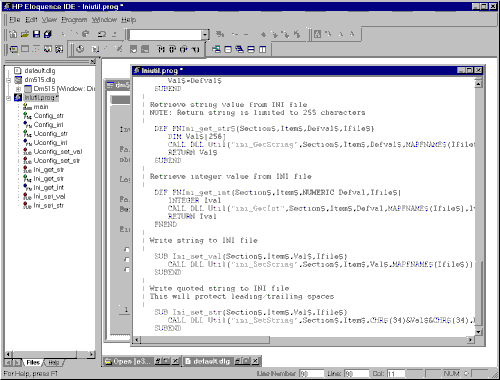
The image below shows the Application Window in a typical situation.
Please click on the image to have a look at the image at full size.
The image consists of the following components:
- The Application window
- The Menubar
- The Toolbar
- The Browse toolwindow
- The Statusbar
- An open document
- An iconized document
The remaining document provides a detailed description of each
element.
The Application window
The Application Window provides a framework for the whole application.
All application windows are normally contained in the Application
windows. It also contains the Application Menu Bar and Status Bar.
Within the Application window, one childwindow is the active
window (it has the keyboard focus). The active window is usually
displayed with an enhanced title bar (as defined by your Windows
configuration) and may obscure other childwindows.
The active childwindow takes over global application ressources,
which are shared by all application windows such as the TitleBar,
the MenuBar and the StatusBar.
The Application TitleBar
The Application TitleBar reflects the TitleBar of the active
ChildWindow.

It consists of the following components:
- The application icon
- The application title
- The title of the active child window
- An asterisk indicates, that the active child window has been modified.
The Menubar
The actual contents of the the Menubar depends on the active
child window. In the Windows MDI model, the topmost child window
provides the active Menubar for the application.
The Menubar consists of Menu topics ("menu panes") which logically
group the available options.
The following menu panes are always available:
| File
| This menu pane provides access to functions affecting
entire files like File New, File Open, Print Setup and the list
of last recently accessed files.
Please refer to the File Management
document for more information.
|
|---|
| View
| This menu pane provides access to the tool windows.
|
|---|
| Program
| This menu pane provides access to the program development and
debugging functions.
|
|---|
| Window
| This menu pane provides access to window layout functions
and the list of child windows.
|
|---|
| Help
| This menu pane provides access to the online help.
|
|---|
The Application Statusbar
While the actual layout of the the StatusBar depends on the active
child window the following image reflects a typical situation:

The StatusBar contains of the following elements:
- The two leftmost elements reflect the cursor position of
the active child window. This element only available when
a text window is on top. When it is visible, you can set the
cursor position in the associated window by overwriting the
value and pressing the Return key.
- The next three elements reflect the keyboard status of the
topmost child window. It contains the following indicators:
| OVR
| This is visible, when the active window is in
Overwrite mode. When not visible, the default imput mode
(usually insert mode) is used.
|
|---|
| CAP
| This is visible, when the SHIFT LOCK keyboard mode
is active. (The acronym actually refers to CAPS LOCK - Capitals Lock -
which is different as it only affects the alpha keys.
But CAPS Lock is in common use in the Windows environment.)
|
|---|
| NUM
| This is visible, when the NUM LOCK keyboard mode is active.
|
|---|
- The color marker indicates an active network connection.
When the marker is Yellow, the network connection is is use (data are transmitted
or a response is expected). When the marker is Green, the network connection is
idle, but still connected. When the network connection times out, the indicator
disappears.
- The rightmost field contains the word "RUN" when a debugging
session is active.
Toolbars
Toolbars are intended to provide accelerated access to common
used function. Instead of navigating through the menu bar, you can
execute them with a single mouse click.
They provide a graphical representation of the associated function.
The toolbar actually consists of toolbar windows which contain
the actual toolbar buttons.
Each toolbar window can be
- hidden or visible
- placed in a toolbar area anywhere at the border of the
Application window.
- made a separate window ("undocked")
The image below shows the (undocked) Edit Toolbar window as an example.
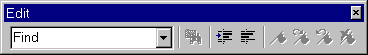
The Eloquence Development Environment provides the following
Toolbar windows:
| File
| File related functions, usually found in the File menu pane.
|
|---|
| Edit
| Editing functions, usually found in the Edit menu pane.
|
|---|
| Attributes
| Program character attributes, such as inverse or underlined.
|
|---|
| View
| View functions, usually found in the View menu pane.
|
|---|
| Program
| Program development functions, usually found in the Program
menu pane.
|
|---|
| Window
| Window geometry functions, usually found in the Window
menu pane.
|
|---|
The Browser Toolwindow is the most fundamental and visible one of
a set of Toolwindows which are included in Eloquence Development
Environment. It serves a dual purpose:
- When the Help tab is selected, it provides access to the
available online help.
- When the Files tab is selected, it reflects the list of editor
windows. With program files it additionally displays the program
structure.
If the Browse Toolwindow is invisible, you can make it visible
by selecting the Browse Menu item form the View menu pane
or pressing the associated accelerator key ALT+1.
The mode can be switched by selecting the corresponding tab
at the lower end of the Browse Toolwindow.
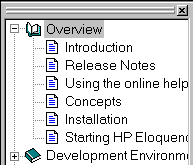
The Documentation Browser
By switching into Documentation mode, you can browse the available
online documentation. The documentation list is not limited to
the static Eloquence documentation, you can easily add you own
documentation to this list and it will be part of the
Development Environment.
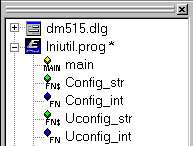
The Source Browser
All files loaded into an editor window have a corresponding entry
in the Browse Toolwindow - it's symbolized by a folder symbol.
When an editor window holds a Eloquence Program, you can
open the folder (this is symbolized by the leading + symbol)
and the list of program segments becomes visible.
Double clicking on the folder symbol will bring the associated
client window on top. Double clicking on a segment name will
additionally position the cursor at the beginning of that section.
Recompiling a program will update its section list.
This is a real live saver if you ever had to jump between
different segments (in even different files) while editing a
program.
© Copyright 1997 Hewlett-Packard GmbH. All rights reserved.
Revision: 98/02/18
 The Eloquence Development Environment
The Eloquence Development Environment